Self Assessment
In post-secondary education, students are used to the age-old practice of handing in an assignment and nervously waiting till it is returned with a grade attached. Flipping this process and encouraging self-assessment encourages students to be a realistic judge of their own work and how to make room to improve. When students become more self-aware about their learning and can take steps to make change, this is motivating and helps them to develop self-directed learning qualities that will benefit them after college life is done.
Self-assessment not only increases student self-awareness but supports the student to set clear goals on how to improve and strive towards next steps in the learning process. Self-assessment can be used in both formative and summative ways using ideas from the examples below. As you read, consider how you might incorporate some of these into your course to support student self-assessment.
Strategies to Promote Self-Assessment
Wrappers
Watch this video to the 5‑minute mark to learn more about self-assessment
This guide from Cornell provides many examples of how self-assessment can be used using something called “wrappers” for homework or for an exam. The intent here is to have the student work through the questions before and after the assignment/exam. Having students reflect on what went well and how preparation might change based on this idea also supports metacognition.
Cornell University, Center for Teaching Innovation: Self-Assessment
Teach Anywhere also has information and examples for you to work from:
- Cognitive Wrappers – Ideas for NIC Instructors – PDF Version
- Cognitive Wrappers: Using Metacognition and Reflection to Improve Learning – Jose Bowen Website
- Exam Wrappers – Carnegie Mellon University Teaching and Learning Centre Site
- Assignment Wrapper – Word – Short Version
- Assignment Wrapper – Word – Long Version
Rubrics
Rubrics can aid in the self-assessment process. This helps students identify areas for improvement and take ownership of their learning process, providing a clear framework to evaluate their own work and gain an understanding of high-quality performance.
The most common rubrics are:
- Analytic rubric: Breaks down each assessed component and provides feedback on each.
- Holistic rubric: Evaluates the entire work, looking at overall quality and performance.
- Single point rubric: Simplified version of analytic rubric, making it easier for students to interpret.
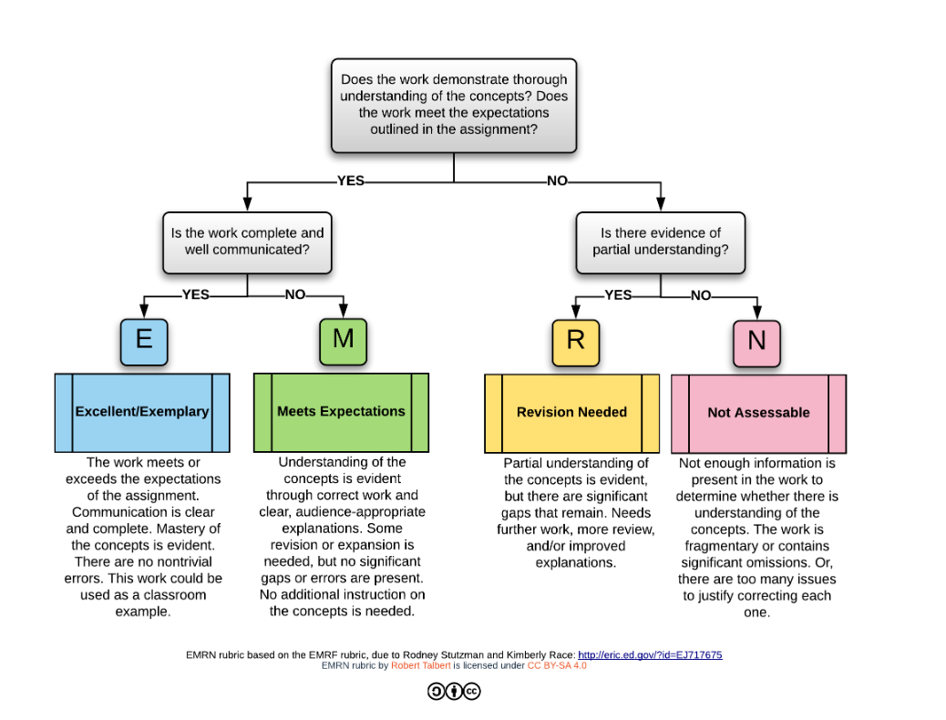
- EMRN rubric: 4 level rubric (see below)
To explore more, begin here:
- McGill University: Rubrics: The Basics
- University of Waterloo: Rubrics: Useful assessment tools
- Carlton: – Examples
- Western University: Examples and links to other sites
- Conestoga: Rubrics